iv injection
₹120
iv injection
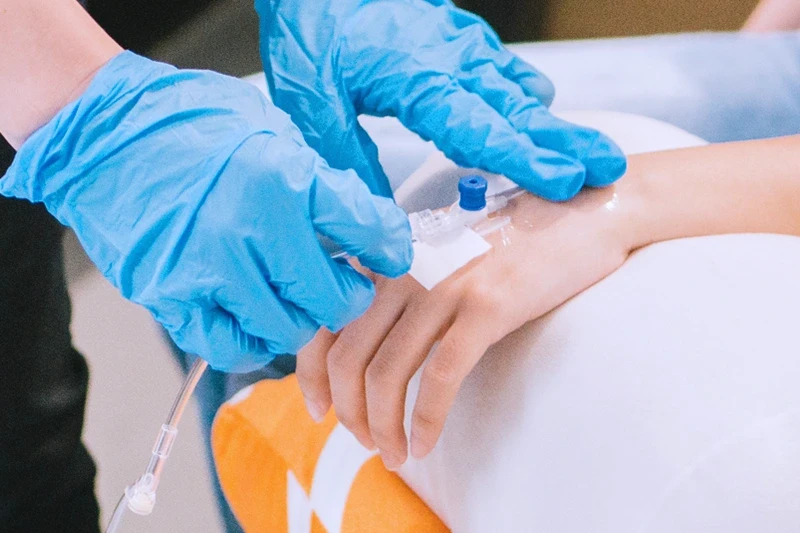
An intravenous (IV) injection is the process of administering medication or fluids directly into a vein, typically through a needle or catheter. This method allows for rapid and complete absorption of the substance into the bloodstream, making it a common choice for delivering medications, fluids, and even blood products.
What is intravenous (IV) injection?
-
Direct Delivery: IV injections involve inserting a needle or catheter into a vein and introducing a substance directly into the bloodstream.
-
-
Rapid Absorption: This route ensures immediate and complete systemic availability of the substance, bypassing the need for absorption through other tissues.
-
Common Uses: IV injections are frequently used for administering medications, fluids, blood transfusions, and nutritional support.
Key Benefits:
-
Fast Action: IV injections allow for a rapid onset of the substance's effects due to the direct route into the bloodstream.
-
Accurate Dosage: The ability to deliver a precise dose directly into the circulation is a significant advantage.
-
Bypass Absorption: IV injection bypasses the absorption process, which can be beneficial when dealing with medications that are poorly absorbed through other routes.
Differentiation from other injections:
-
Intramuscular (IM) Injection: IM injections are administered into the muscle tissue, which has a slower absorption rate compared to IV.
-
Subcutaneous Injection: Subcutaneous injections are given under the skin, also with a slower absorption rate than IV.
In essence, IV injection is a crucial method in healthcare for quickly and effectively delivering substances directly into the bloodstream for various medical purposes.
 Nurse
Nurse
 Blog
Blog
 Home
Home
 My Profile
My Profile
 Nurse Login
Nurse Login